
Bad (or malicious) bots are software applications that run automated tasks with malicious intent including criminal activities such as fraud and outright theft. Fraudsters, attackers, unethical competitors, and bad actors with various motivations often carry out a wide range of malicious activities and attacks by deploying malicious bots on websites, mobile apps, and APIs.
Some of the types of bad bots are DDoS bots, which disrupt a website or online service by overwhelming it with traffic from multiple sources; account takeover bots, which use stolen credentials to access users’ online accounts; web content scraping bots, which copy and reuse website content without permission; and social media bots, which spread fake news and propaganda on social media platforms.
In contrast to bad bots, good bots are software applications that run automated tasks with beneficial purposes over the internet. They help improve the functionality and performance of websites, mobile apps, and APIs. They also provide useful services and information to users. Some of the types of good bots are search engine bots, which crawl through web content to index information for search engines; travel aggregator bots, which check and gather information on flight details and hotel room availabilities; business intelligence bots, which analyze product reviews and social media comments to provide insights on brand perception; and chatbots, which interact with users via natural language to provide customer service or entertainment.
Web Scrapers
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites using automated software or bots. Scraping can have both positive and negative impacts on businesses, depending on how it is used. On one hand, web scraping can help businesses automate tasks, gain insights, and create value from data. For example, web scraping can be used to find leads, compare prices, monitor trends, and conduct market research. On the other hand, web scraping can also harm businesses by stealing their content, compromising their competitive advantage, or exposing them to fraud and cyberattacks. For example, web scraping can be used to copy content, create fake e-commerce sites, deliver malware, or perform ad fraud.
Credential Stuffing Bots
Credential stuffing is a type of cyberattack in which hackers use stolen usernames and passwords from one website to access user accounts on another website. Hackers obtain these credentials from data breaches or the dark web and use bots to try them on multiple websites at once.
Credential stuffing can have a negative impact on businesses, as it can lead to:
Fraud:
Hackers can use compromised accounts to order high-value products or services, either for their own use or for reselling, which can result in chargebacks, fines, and loss of revenue for businesses. Hackers can also use credential stuffing to validate stolen credit card data or check gift card balances.
Account takeover:
Hackers can gain access to user accounts and personal data, such as credit card numbers, addresses, loyalty points, gift cards, and similar forms of stored value. They can use these accounts to make fraudulent purchases, sell access to other hackers, or impersonate users for phishing or identity theft purposes.
Espionage and theft:
Hackers can use credential stuffing to target employee or administrator accounts and gain access to sensitive business information, customer data, financial records, and much more. They can use this information for blackmail, extortion, or sale to competitors or other criminals.
Reputational damage:
Credential stuffing attacks can erode customer trust and loyalty, as well as damage the brand image and reputation of businesses. Customers may blame businesses for not protecting their accounts or data, and may switch to competitors or file lawsuits. Businesses may also face regulatory penalties or sanctions for failing to comply with data protection laws.
According to the Ponemon Institute, credential stuffing attacks can cost businesses from $6 million to $54 million annually. Therefore, businesses should implement effective bot management solutions and cybersecurity measures to prevent credential stuffing attacks and protect their customers and data.
DDoS Bots
DDoS bots are used to carry out Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. A DDoS attack is a malicious attempt to disrupt the normal traffic of a targeted server, service or network by overwhelming the target or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic. These attacks can have a significant impact on businesses.
For example, if a company’s website or online shop goes offline due to a DDoS attack, it can quickly start to lose money as orders and requests can’t be processed. DDoS attacks can also result in loss of reputation for businesses and organizations that are impacted by a hack. Hackers may also combine DDoS with other types of cyberattacks, resulting in data loss.
DDoS attacks are becoming larger and more complex in nature. According to Gcore, in 2022, the number and volume of DDoS attacks will roughly double compared to 2021. The average attack power will grow from 150–300 Gbps to 500–700 Gbps. Both ordinary users and businesses in any industry—fintech, gaming, e-commerce, and others—are being targeted for DDoS attacks.
Spam Bots
Spam bots are automated programs that mimic genuine user behavior to spread content. Some bots are beneficial and can improve a user’s online experience. However, many spam bots are malicious and are often used to spread harmful or false content.
Spam bots can have a significant impact on businesses. For example, they can damage a company’s reputation by impersonating the company or one of its employees. They can also cause financial loss and data breaches. Responding to spam bots can cost an organization significantly in terms of time, effort, and expense in combating them.
Some common signs of bad bot activity are:
- Abnormally high pageviews: Certain bot attacks will try to overwhelm your servers
- Unusually high bounce rate: Every bot has a goal
- Junk conversions
- Abnormal session durations: Sessions in the range of milliseconds are suspicious, as are abnormally long sessions
- Spikes in traffic from unknown locations
Some tools and techniques to detect bad bots include:
- Separating bots from people by measuring communication frequency: Bots of all types tend to communicate continuously with their targets.
- Distinguishing between bots within browsers.
- Analyzing the payload.
- Distinguishing between browsers and other clients: Simply knowing a bot exists on a machine alone won’t help very much: as we said most machines generate some bot traffic.
- Target analysis: What URLs and endpoints are bots attacking?
The Importance of Having a Comprehensive Bot Management Strategy
Having a comprehensive bot management strategy is crucial for businesses to protect themselves from automated threats. A good bot management strategy can help detect and mitigate these threats, protecting critical applications and APIs while ensuring a positive user experience for customers. An effective bot management product must have a strong detection layer that features several detection methods to analyze web traffic from different angles. This helps differentiate legitimate traffic from malicious traffic and detect potential threats like credential stuffing and inventory hoarding.
Bot management isn’t just about detecting threats; it’s also about having a tailored response strategy. Too often, we see a strong detection strategy combined with a weak response strategy (or vice versa). If you have a strong detection strategy but a weak response strategy, you may perceive bots that get through as false negatives—in reality, the detections worked but your response strategy allowed the bots through.
Having a comprehensive bot management strategy is essential for businesses to protect themselves from automated threats and ensure a positive user experience for their customers.
Radware has several solutions that can help safeguard your business from bad bots. Radware’s Bot Manager solution is part of the Radware 360° Cloud Application Protection Service and includes enhancements that provide comprehensive protection to organizations and prevent malicious actors from executing automated attacks.
Radware’s Bot Manager now includes a new set of crypto mitigation algorithms. Inspired by blockchain methodologies, the new algorithms create CPU-intensive, browser-based challenges that gradually increase in difficulty. The mitigation is immune to third-party tampering while providing a frictionless, CAPTCHA-free user experience.
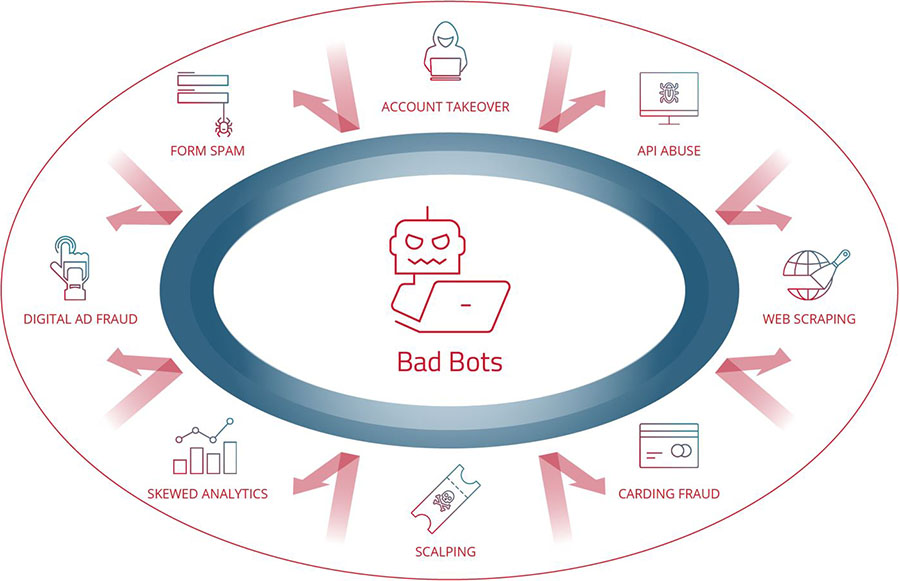
Bad bots can have a significant impact on businesses. They affect website load time, steal confidential organizational and customer information, impact site security, and negatively influence brand reputation. Malicious bots inflict material financial costs on enterprises by taking over customer accounts through credential stuffing and credential cracking attacks, slowing web and application performance through scraping, frustrating customers and preventing purchases through scalping and inventory hoarding, and furthermore, stealing payment and gift card, loyalty points, and leading to chargebacks and fines.
Take Action and Protect Your Business With Radware's Bot Management Solution
It's more important than ever to protect your business from the threat of bad bots. Radware's bot management solutions can help safeguard your business from these threats by detecting and mitigating automated attacks. With Radware's industry-leading technology and expertise, you can be sure that your critical applications and APIs are protected, and your customers have a positive user experience.