The need for speed is at the heart of organizations’ strategic decisions about digital transformation. Faster time to market for revenue-generating applications is a competitive advantage. New technologies, frameworks and paradigms emerge to accelerate productivity, efficiency and cost reduction.
Yet these also create blind spots calling for new threats. Neglect can be very costly, as the average cost estimation of a cyberattack is $1.7M for large enterprises and roughly $500,000 for smaller businesses.
Radware’s 2019-2020 Global Network and Application Security Report investigated how organizations cope with the multi-dimensional transformation of information networks today, focusing on three main challenges: security across multiple cloud infrastructures, securing data in microservices environments, and preparations for the rollout of 5G networks. An analysis of a global survey allows understanding 2019’s trends to better prepare for 2020’s threat landscape.
2019 Threat Landscape
Only 6% of respondents claimed to make it through 2019 without a single attack. This doesn't come as much surprise; cyberattacks are a fact of life and are discussed on a weekly basis among 72% of executives. What is surprising is the 42% increase in attacks businesses attribute to nation-state originated activities.
[You may also like: Nation-State Attacks: Motivations & Consequences]
36% of the companies in North America report nation-state attribution. The most common attacks were malware and ransomware, rising back to 2017 levels and hitting three out of every five organizations. In addition, one in three experienced a DDoS attack in 2019, with 91% suffering an application layer attack (HTTP/S flood, low-and-slow, etc.).
Multi-Cloud Security Management
75% of organizations now use a public cloud environment. Of those, most (60%) prefer using multiple cloud providers, mainly to avoid putting all eggs in one basket. However, this requires a bigger effort not only in necessary adjustments to make the most of each infrastructure, but also in terms of maintaining a solid, consistent security posture.
[You may also like: Cloud Migration: Times, They Are A-Changin’]
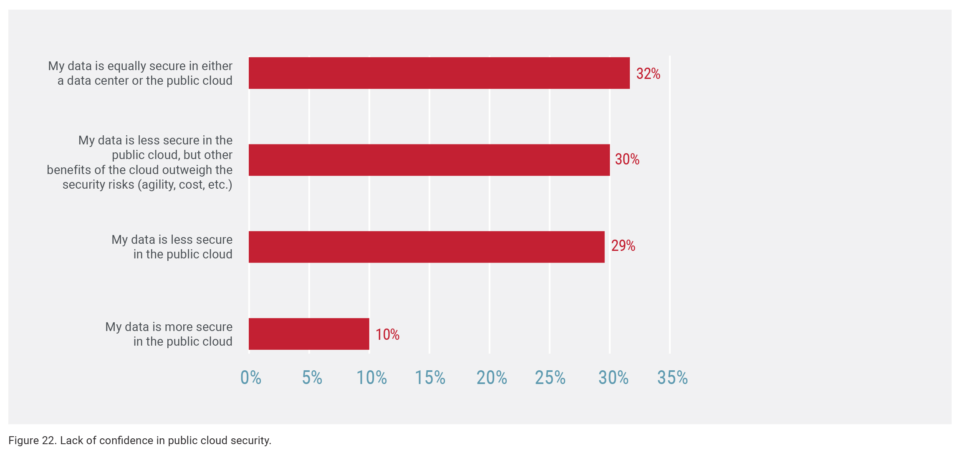
In 2019, many of the publicly reported data breaches involved hacking into the cloud environment, mostly by obtaining unauthorized access or stealing account credentials. We were surprised to find that while only 10% of respondents felt their data is secure in a public cloud environment, 30% agree, but say the benefits outweigh potential risks. Looking ahead to 2020, such risks include web application intrusions-the biggest threat to companies’ cloud environments, followed by credential theft (27% and 20%, respectively).
Security at the Speed of Application Development
The adoption of microservices, containers and other ways to utilize computing more efficiently, as well as the flexibly require organizations to rethink their security strategy. End-to-end automation, increased consumption of ephemeral components and the reliance on APIs (also between services, “east-west”) reduces the visibility and control over applications and microservices.
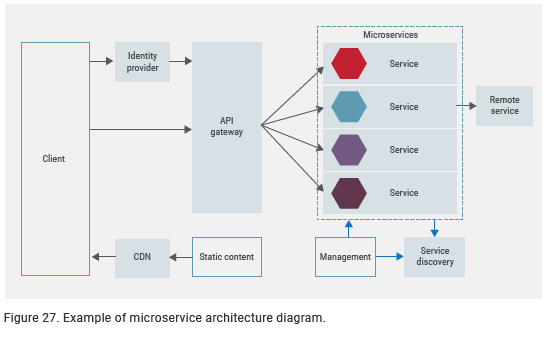
This is further confirmed in our 2019 Web Application Security report, which found that:
- 88% reported attacks against their applications, 81% against their APIs
- 68% believe microservices architecture is more secure by default
- 61% integrated DevSecOps into their application development division
- 75% suffered bot attacks, such as account takeover, scraping and more
- Two thirds of applications undergo weekly changes, but security is not as adaptive
[You may also like: Agile Security Is Now A Reality]
The Promise of 5G Rollouts Isn't Security
87% of telecom companies are planning to rollout 5G networks before 2022. The promise of blazing fast data speeds and lower latency services on mobile networks that enable large-scale deployments of IoT devices is highly anticipated. However, most aren’t prepared to secure 5G networks; only 58% of service providers say they are prepared and other verticals are woefully under-prepared (only 16%–34% are ready).
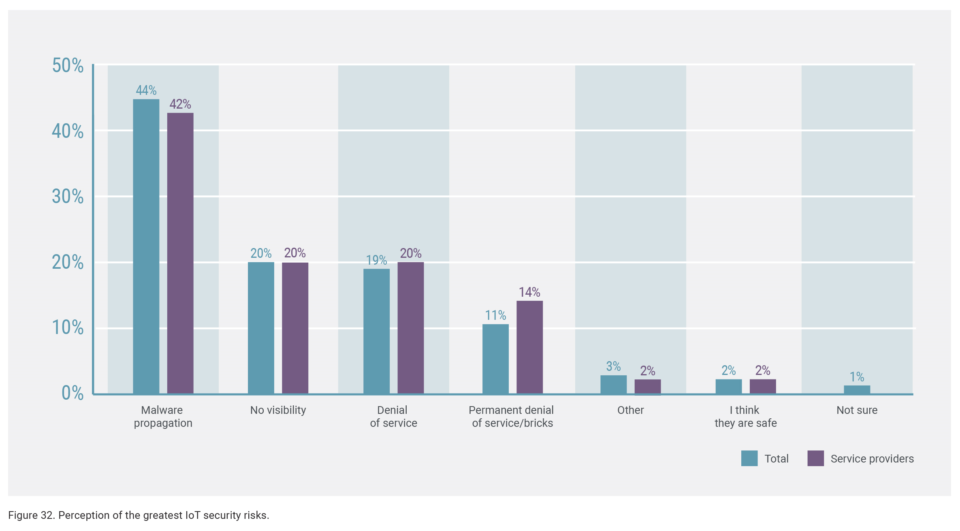
When it comes to IoT connected devices, 44% of respondents said malware propagation was their top concern, while lack of visibility and Denial of Service attacks both followed at 20%.
Blind Spots Everywhere
Security professionals feel the pressure to keep up
with the speed of business, but at what cost? Uncertainties about where
vulnerabilities are hiding in dispersed information networks abound.
Limited visibility across entire network ecosystems
proved to be a significant issue. How do you protect what you can’t see?
- 22% don’t even know if they were attacked
- 27% of those that were attacked don’t know the hackers’ motivations
- 38% aren’t sure if an IoT botnet hit their networks
- 46% aren’t sure if they suffered an SSL-based DDoS attack
- 13% don’t know how a cyberattack impacted their business
- 30% do not monitor east-west traffic
[You may also like: 10 Commandments for Securing Microservices]
Radware’s 2019–2020 Global Application & Network Security Report combines statistical research and front-line experience to identify cybersecurity trends, from Radware’s proprietary Threat Deception Network as well as real-life cases our ERT experts have battled this past year. The report is designed for the entire security community and will help in understanding the following:
- The threat landscape—who the attackers are, their motives and tools
- Potential impact on your business, including associated costs of different cyber-attacks
- How your preparedness level compares to other organizations
- Experiences of organizations in your industry
- Emerging threats and how to protect against them
- Predictions for 2020

Read Radware's “2019-2020 Global Application & Network Security Report” to learn more.
Download Now